Web Services
The CRDS servers support a JSONRPC based service mechanism which enables remote users to make calls to the CRDS server without installing the CRDS Python based client library. See http://json-rpc.org/wiki/specification for more details on the JSONRPC protocol.
Users of the CRDS client library can access these JSONRPC functions using the crds.client module. Examples follow below.
Context Information
The CRDS context is the version of CRDS rules used to select reference files.
The default CRDS context is maintained on the CRDS server and reported by
the function get_default_context(). Institutional pipelines which are operating
decoupled from the CRDS server can post their actual cached context to the CRDS
server for retrieval by get_remote_context().
Centralized Default
get_default_context(observatory)
get_default_context() returns the name of the context which is
currently in use by default in the archive pipeline, e.g. ‘jwst_0001.pmap’.
This value is set and maintained on the CRDS Server. The actual pipeline context
differs from this commanded valuer until the pipeline is synchronized with the CRDS
server using cron_sync.
The commanded default can be obtained using the CRDS client library as follows:
>>> from crds import client
>>> client.get_default_context('hst')
'hst_1006.pmap'
>>> from crds import client
>>> client.get_default_context('jwst')
'jwst_0101.pmap'
>>> from crds import client
>>> client.get_default_context('roman')
'roman_0037.pmap'
See the explanation of JSONRPC requests and responses below for a language and library neutral example of calling the same CRDS web service using the command line program “curl”.
Pipeline Echo
get_remote_context(observatory, pipeline_name)
get_remote_context() returns the name of the context last reported as
synced by the specified pipeline_name (e.g. ‘jwst-ops-pipeline’). This is
the value stored in a pipeline’s CRDS cache and echoed back to the CRDS server
when the cache is synchronized. Since this value is inapplicable if a pipeline
is run in “remote” mode computing best references on the CRDS Server, the
generally preferred value is from get_default_context() since it always
reflects the intended latest context regardless of the pipeline’s CRDS
mode. For JWST, get_default_context() retrieves the “build” context associated
with the version of JWST pipeline calibration software installed locally,
which may or may not differ from the “latest” context.
This ensures compatibility between reference files and calibration software.
The actual default context for a pipeline can be obtained as follows:
>>> from crds import client >>> client.get_remote_context('jwst', 'jwst-ops-pipeline') 'jwst_0101.pmap'
Context History
CRDS makes the history of contexts which have been activated in the pipeline as
the latest context via the get_context_history() web service:
>>> client.get_context_history("jwst") [('2012-09-06 00:00:00', 'jwst.pmap', 'Bootstrap mappings'), ('2012-09-27 00:00:00', 'jwst_0000.pmap', 'First rules and references from jwst_gentools stub development cloning.'), ('2013-04-13 00:00:00', 'jwst_0001.pmap', 'Linearity and dark files.'), ('2013-07-31 00:00:00', 'jwst_0002.pmap', 'Dark and Mask files.'), ('2013-09-04 00:00:00', 'jwst_0003.pmap', 'Absolute Calibration (photom) additions and replacements.'), ('2013-11-25 09:00:03', 'jwst_0005.pmap', 'set by system'), ('2014-03-19 10:51:19', 'jwst_0012.pmap', 'Updated for META.INSTRUMENT.TYPE switch to META.INSTRUMENT.NAME\r\nNew linearity files for all instruments\r\nNew saturation files and rmaps for all instruments'), ... ('2015-11-18 12:58:13', 'jwst_0105.pmap', 'Declared various EXP_TYPE as N/A for 15 WCS types for MIRI, NIRCAM, NIRSPEC. Replacement MIRI distortion references for ticket #238.') ]
Each entry in the context history is a list/tuple of form: (start_date, context, description).
Adjacent entries are consecutive, the start date of the one context is the end date of the previous context.
The context history is in first-to-last order and it is possible that the context will be regressed to a prior version; consequently, there is no guarantee that context names will monotonically increase. At times several file submissions and created contexts are activated en masse via the last created context; consequently, there is no guarantee that pmap serial numbers will increase or decrease by one.
File Information
The CRDS server maintains a catalog of basic metadata for the rules and reference files managed by CRDS. Catalog information cab be
Single File Metadata
get_file_info(pipeline_context, filename)
Return a dictionary of CRDS catalog information about filename. For instance:
>>> from crds import client >>> client.get_file_info("jwst", "jwst_miri_flat_0023.fits") {'activation_date': '2014-09-25 18:30:27', 'aperture': 'none', 'blacklisted': 'false', 'change_level': 'severe', 'comment': 'cdp-2 from fm testing', 'creator_name': 'jwst build 3 team', 'deliverer_user': 'homer', 'delivery_date': '2014-09-20 07:55:56', 'derived_from': 'none', 'description': 'all references from jwst build 3 delivery 2. update miri flats, fringes, straymasks, resets, lastframes, nirspec flat.', 'filekind': 'flat', 'instrument': 'miri', 'name': 'jwst_miri_flat_0023.fits', 'observatory': 'jwst', 'pedigree': 'ground', 'reference_file_type': 'flat', 'rejected': 'false', 'replaced_by_filename': '', 'sha1sum': '3f0c92aae539cb67f8e8823cc6815130018948f7', 'size': '10592640', 'state': 'latest', 'type': 'reference', 'uploaded_as': 'jwst_miri_flat_0016.fits', 'useafter_date': '2050-01-01 00:00:00'}
Multiple File Metadata
get_file_info_map(observatory, files=None, fields=None)
get_file_info_map() is a multi-file version of get_info_map() which returns
the information for several files with one call. If files is not specified
then get_file_info_map() returns info for all files:
>>> from crds import client >>> client.get_file_info_map("jwst") {'jwst.pmap': {'activation_date': '2012-07-31 00:00:00', 'aperture': 'none', 'blacklisted': 'false', 'change_level': 'severe', 'comment': 'none', 'creator_name': 'todd miller', 'deliverer_user': 'crds', 'delivery_date': '2014-03-26 08:49:23', 'derived_from': 'created by hand 07-31-2012', 'description': 'initial mass file import', 'filekind': '', 'history': 'none', 'instrument': '', 'name': 'jwst.pmap', 'observatory': 'jwst', 'pedigree': '', 'reference_file_type': '', 'rejected': 'false', 'replaced_by_filename': '', 'sha1sum': 'caf080abe09236165885f383045c59e8957a80ce', 'size': '392', 'state': 'archived', 'type': 'mapping', 'uploaded_as': 'jwst.pmap', 'useafter_date': '2012-07-31 00:00:00'}, ... }
Returns the info:
{ filename : { info, ... }, ... }
on files of observatory.
fields can be used to limit info returned to specified keys:
['activation_date', 'aperture', 'blacklisted', 'change_level', 'comment', 'creator_name', 'deliverer_user', 'delivery_date', 'derived_from', 'description', 'filekind', 'instrument', 'name', 'observatory', 'pedigree', 'reference_file_type', 'rejected', 'replaced_by_filename', 'sha1sum', 'size', 'state', 'type', 'uploaded_as', 'useafter_date']
If fields is not specified then get_file_info_map() returns all fields.
Best References
Single Header
get_best_references(context, header, reftypes)
get_best_references() matches a set of parameters header` against the lookup
rules specified by the pipeline mapping context` to return a mapping of
type names onto recommended reference file names.
A suitable context` string can be obtained from get_default_context() above,
although any archived CRDS context file can be specified.
The header` parameter of get_best_references is nominally a JSON object which
maps CRDS parkey names onto dataset file header values. CRDS parkey names can
be located by browsing reference mappings (.rmap’s) and looking at the parkey
header parameter of the rmap.
For HST, GEIS or FITS header keyword names are supported. reftypes should be a json array of strings, each naming a single desired reference type. If reftypes is passed as null, recommended references for all reference types are returned. Reference types which are defined for an instrument but which are not applicable to the mode defined by header are returned with the value NOT FOUND n/a.
Example JSON for reftypes might be:
["amplifier","mask"]
Because get_best_references determines references for a list of types, lookup errors are reported by setting the value of a reference type to “NOT FOUND “ + error_message. A value of “NOT FOUND n/a” indicates that CRDS determined that a particular reference type does not apply to the given parameter set.
For JWST, the rmap parkeys (matching parameter names) are currently specified as JWST stpipe data model dotted identifiers. Example JSON for the get_best_references header parameter for JWST is:
{"meta.instrument.type":"fgs", "meta.instrument.detector":"fgs1", "meta.instrument.filter":"any"}
It is also possible to use the equivalent FITS header keyword, as defined by the data model schema, to determine best references:
{"instrume":"fgs", "detector":"fgs1", "filter":"any"}
For Roman, the rmap parkeys (matching parameter names) are currently specified as Roman Datamodels dotted identifiers. Example JSON for the get_best_references header parameter for Roman is:
{"roman.meta.exposure.type":"grism", "roman.meta.instrument.detector":"wfi01", "roman.meta.exposure.ma_table_number":"any"}
Multiple Headers
get_best_references_by_header_map(context, header_map, reftypes)
This service is an adaptation of get_best_references() to support returning
best references for multiple datasets with a single service call. All
parameters are as for get_best_references() with the modification that header
above is replaced with a mapping from multiple dataset ids to their
corresponding headers, i.e. header_map:
{ dataset_id : header, ... }
The return value is likewise adapted to return best references for multiple datasets:
{ dataset_id : best_references, ... }
Where dataset_id is nominally an HST IPPPSSOOT id (e.g. ‘I9ZF01010’), JWST or Roman
dataset identifier (TBD). Since dataset_id is only a keyword not used in best
references computations, it can be any unique abstract identifier consisting of
alphanumeric characters, period, colon, hyphen, or plus sign of 128 characters
or less.
Selection Parameters
get_required_parkeys(context)
Return a mapping from instruments to lists of parameter names required to
compute bestrefs under context, i.e. matching header keys:
{ instrument : [ matching_parkey_name, ... ], ... }
In CRDS the matching parameters are defined by each set of rules, e.g. for
one HST context hst_0366.pmap the reference file selection parameters
for all instruments are as follows:
{'acs': ['INSTRUME', 'APERTURE', 'ATODCORR', 'BIASCORR', 'CCDAMP', 'CCDCHIP', 'CCDGAIN', 'CRCORR', 'DARKCORR', 'DATE-OBS', 'DETECTOR', 'DQICORR', 'DRIZCORR', 'FILTER1', 'FILTER2', 'FLASHCUR', 'FLATCORR', 'FLSHCORR', 'FW1OFFST', 'FW2OFFST', 'FWSOFFST', 'GLINCORR', 'LTV1', 'LTV2', 'NAXIS1', 'NAXIS2', 'OBSTYPE', 'PCTECORR', 'PHOTCORR', 'REFTYPE', 'RPTCORR', 'SHADCORR', 'SHUTRPOS', 'TIME-OBS', 'XCORNER', 'YCORNER'], 'cos': ['INSTRUME', 'ALGNCORR', 'BADTCORR', 'BRSTCORR', 'DATE-OBS', 'DEADCORR', 'DETECTOR', 'EXPTYPE', 'FLATCORR', 'FLUXCORR', 'LIFE_ADJ', 'OBSMODE', 'OBSTYPE', 'OPT_ELEM', 'REFTYPE', 'TDSCORR', 'TIME-OBS', 'TRCECORR', 'WALKCORR'], 'nicmos': ['INSTRUME', 'CAMERA', 'DATE-OBS', 'FILTER', 'NREAD', 'OBSMODE', 'READOUT', 'REFTYPE', 'SAMP_SEQ', 'TIME-OBS'], 'stis': ['INSTRUME', 'APERTURE', 'BINAXIS1', 'BINAXIS2', 'CCDAMP', 'CCDGAIN', 'CCDOFFST', 'CENWAVE', 'DATE-OBS', 'DETECTOR', 'OBSTYPE', 'OPT_ELEM', 'REFTYPE', 'TIME-OBS'], 'wfc3': ['INSTRUME', 'APERTURE', 'ATODCORR', 'BIASCORR', 'BINAXIS1', 'BINAXIS2', 'CCDAMP', 'CCDGAIN', 'CHINJECT', 'DARKCORR', 'DATE-OBS', 'DETECTOR', 'DQICORR', 'DRIZCORR', 'FILTER', 'FLASHCUR', 'FLATCORR', 'FLSHCORR', 'PHOTCORR', 'REFTYPE', 'SAMP_SEQ', 'SHUTRPOS', 'SUBARRAY', 'SUBTYPE', 'TIME-OBS'], 'wfpc2': ['INSTRUME', 'ATODGAIN', 'DATE-OBS', 'FILTER1', 'FILTER2', 'FILTNAM1', 'FILTNAM2', 'IMAGETYP', 'LRFWAVE', 'MODE', 'REFTYPE', 'SERIALS', 'SHUTTER', 'TIME-OBS'] }
The required parkeys can be used to reduce a complete file header to only those keywords necessary to select references under the given context.
Valid Dataset IDs
get_dataset_ids(context, instrument)
CRDS interacts with the archive to obtain matching parameters to compute best references for particular datasets. Each parameter set corresponds to a dataset ID. A list of the valid dataset IDs with respect to a particular CRDS context (or date) can be obtained as follows.
To obtain current best references, specify the context using a date:
>>> get_dataset_ids("2016-01-01T00:00:00", "miri")
['JW80500017001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500017001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT',
'J80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT',
'JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT',
'JW80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG:JW80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG',
'JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFULONG:JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFULONG',
'JW80500009001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE:JW80500009001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE',
'JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG:JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG',
'JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFUSHORT',
'JW80500003001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE:JW80500003001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE',
'JW80500018001_02101_00003.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500018001_02101_00003.MIRIFUSHORT']
>>> get_dataset_ids("2022-01-01T00:00:00", "wfi")
['R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01:R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01',
'R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI01:R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI01',
'R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI16:R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI16',
'R0000201001001001003_01101_0001_WFI01':'R0000201001001001003_01101_0001_WFI01']
Alternately, the abstract default context can be specified as “<project>-latest”, as in:
>>> get_dataset_ids("jwst-latest", "miri")
['JW80500017001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500017001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT',
'J80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT',
'JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT',
'JW80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG:JW80500020001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG',
'JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFULONG:JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFULONG',
'JW80500009001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE:JW80500009001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE',
'JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG:JW80500018001_02101_00001.MIRIFULONG',
'JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500018001_02101_00002.MIRIFUSHORT',
'JW80500003001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE:JW80500003001_02101_00001.MIRIMAGE',
'JW80500018001_02101_00003.MIRIFUSHORT:JW80500018001_02101_00003.MIRIFUSHORT']
>>> get_dataset_ids("2022-01-01T00:00:00", "wfi")
['R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01:R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01',
'R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI01:R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI01',
'R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI16:R0000101001001001001_01101_0001_WFI16',
'R0000201001001001003_01101_0001_WFI01':'R0000201001001001003_01101_0001_WFI01']
Dataset IDs use a specific grammar depending on the mission:
For HST requesting parameters using only the <product_id> returns the parameters associated with the full two part ID for every exposure of the product. Requesting the parameters using only the <exposure_id> returns the references associated with processing that exposure.
<product_id> : <exposure_id>
It’s possible to specify either half of an ID returned by get_dataset_ids() to request matching parameters or best references using the services below.
As can be seen below, currently JWST IDs are redundant and <whole> and <part> are identical. However, conceptually the IDs have that relationship and may be further elaborated and differentiated in later builds (post-jwst-build-7). In such a case, several exposure level IDs (<parts>’s) might have an identical common root (<whole>).
<id> := <whole>:<part> <whole> := <filesetname>:<detector> <part> := <filesetname>:<detector>
It’s possible to specify either half of an ID returned by get_dataset_ids() to request matching parameters or best references using the services below. For JWST, conceptually the same behavior as HST will be preserved, so while either half of an ID will currently return the same parameters, at a future date the <whole> part may return all references associated with all exposures of a single high level product, and the <part> component will only return the references associated with processing that particular exposure.
As can be seen below, currently Roman IDs are redundant and <whole> and <part> are identical. However, conceptually the IDs have that relationship and may be further elaborated and differentiated in later builds. In such a case, several exposure level IDs (<parts>’s) might have an identical common root (<whole>).
<id> := <whole>:<part> <whole> := <filesetname>:<detector> <part> := <filesetname>:<detector>
It’s possible to specify either half of an ID returned by get_dataset_ids() to request matching parameters or best references using the services below. For Roman, conceptually the same behavior as HST will be preserved, so while either half of an ID will currently return the same parameters, at a future date the <whole> part may return all references associated with all exposures of a single high level product, and the <part> component will only return the references associated with processing that particular exposure.
Matching Parameters By ID
get_dataset_headers_by_id(context_specifier, ids, datasets_since)
CRDS fetches best reference matching parameters indirectly from the archive database.
The get_dataset_headers_by_id() function can be used to return the parameters required
to compute best references associated with the specified dataset ids:
context_specifier is a date-based CRDS context specifier, e.g.: jwst_0192.pmap, 2015-05-25T00:00:27, jwst-latest
ids is a list of archive dataset id strings as shown above. A maximum of 200 IDs should be requested per call.
datasets_since is an optional cut-off date for datasets. If specified, only datasets acquired after that date are returned.
An example call using the CRDS Python client is:
>>> get_dataset_headers_by_id("2016-01-01", ['JW96090001004_03101_00001.NRCB2'], None)
{'JW96090001004_03101_00001.NRCB2': {
'META.EXPOSURE.READPATT': 'BRIGHT1',
'META.EXPOSURE.TYPE': 'NRC_IMAGE',
'META.INSTRUMENT.CHANNEL': 'SHORT',
'META.INSTRUMENT.DETECTOR': 'NRCB2',
'META.INSTRUMENT.FILTER': 'F150W2',
'META.INSTRUMENT.NAME': 'NIRCAM',
'META.INSTRUMENT.PUPIL': 'CLEAR',
'META.SUBARRAY.NAME': 'FULL'
}
}
>>> get_dataset_headers_by_id("2021-09-01", ['r0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01'], None)
{'R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01': {
"ROMAN.META.INSTRUMENT.NAME": "WFI",
"ROMAN.META.INSTRUMENT.DETECTOR": "WFI01",
"ROMAN.META.INSTRUMENT.OPTICAL_ELEMENT": "GRISM",
"ROMAN.META.EXPOSURE.MA_TABLE_NUMBER": 1,
"ROMAN.META.EXPOSURE.TYPE": "WFI_GRISM",
"ROMAN.META.EXPOSURE.START_TIME": "2021-09-01T00:02:28"
}
}
AUI Interface for Best References
get_aui_best_references(date, ids)
The CRDS server can compute the best references for a list of data set ids
using the get_aui_best_references() function. The dataset ids must be
compatible with those returned by get_dataset_ids() above. Examples below
are fully functional at this time but actual IDs and parameter sets may change
during the course of development; use get_dataset_ids() documented above to
obtain up-to-date example IDs.
date is a date-based CRDS context specifier, e.g.: jwst_0192.pmap, 2015-05-25T00:00:27, jwst-latest
ids is a list of valid archive dataset ids. For JWST it’s currently natural and supported to use either half (currently identical) of the dataset IDs as specified in get_dataset_ids() above. Using a “half-ID” is shown below. Ultimately the first half will identify a group of exposures and the second half will identify a single exposure in the group. A maximum of 200 ids should be requested per call.
An example call using the CRDS Python client is:
>>> get_aui_best_references("2016-01-01", ['JW82500001003_02102_00001.NRCA1','JW82500001003_02102_00001.NRCA3'])
{'JW82500001003_02102_00001.NRCA1': [True,
['jwst_nircam_ipc_0001.fits',
'jwst_nircam_linearity_0020.fits',
'jwst_nircam_distortion_0001.asdf',
'jwst_nircam_drizpars_0001.fits',
'jwst_nircam_area_0001.fits',
'jwst_nircam_flat_0000.fits',
'jwst_nircam_saturation_0030.fits',
'jwst_nircam_photom_0031.fits',
'jwst_nircam_dark_0030.fits',
'jwst_nircam_gain_0000.fits',
'jwst_nircam_mask_0010.fits',
'jwst_nircam_readnoise_0000.fits',
'jwst_nircam_superbias_0001.fits']],
'JW82500001003_02102_00001.NRCA3': [True,
['jwst_nircam_ipc_0003.fits',
'jwst_nircam_linearity_0022.fits',
'jwst_nircam_distortion_0003.asdf',
'jwst_nircam_drizpars_0001.fits',
'jwst_nircam_area_0001.fits',
'jwst_nircam_flat_0003.fits',
'jwst_nircam_saturation_0032.fits',
'jwst_nircam_photom_0033.fits',
'jwst_nircam_dark_0032.fits',
'jwst_nircam_gain_0002.fits',
'jwst_nircam_mask_0012.fits',
'jwst_nircam_readnoise_0002.fits',
'jwst_nircam_superbias_0003.fits']],
...
}
>>> get_aui_best_references("2019-01-01", ['R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01'])
{'R0000201001001001002_01101_0001_WFI01': [True,
['roman_wfi_area_0002.asdf',
'roman_wfi_dark_0014.asdf',
'roman_wfi_distortion_0012.asdf',
'roman_wfi_flat_0011.asdf',
'roman_wfi_gain_0004.asdf',
'roman_wfi_linearity_0016.asdf',
'roman_wfi_mask_0014.asdf',
'roman_wfi_photom_0010.asdf',
'roman_wfi_readnoise_0005.asdf',
'roman_wfi_saturation_0014.asdf']],
}
The value returned is a mapping from dataset ids to a pair of values. The first value of the id result pair is a boolean with the sense “completed successfully”.
The second value has a variable type depending on the boolean value. If the ID was successful, the second value of the pair is a list of file names. If the ID was unsuccessful, the second value of the pair is a string describing the error:
>>> get_aui_best_references("2016-01-01", ['JW96090001004_03101_00001.NRCB5']) {'JW96090001004_03101_00001.NRCB5': [False, "NOT FOUND dataset ID does not exist 'JW96090001004_03101_00001.NRCB5'"]}
Although it is possible for errors to occur on a per-type basis, for this
interface specific types which result in lookup errors (e.g. flat) are dropped
from the results. The net effect is that the list of files returned includes
only those types that could be successfully assigned with the given context
(date) and parameter set. Types which are assigned the value N/A are also
silently dropped.
Under the hood the get_aui_best_references() function is a language agnostic JSONRPC call
which can be called from the UNIX command line, e.g. by curl as follows:
$ curl -i -X POST -d '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "method": "get_aui_best_references", "params": ["2016-01-01", ["JW80500017001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT"]], "id": 1}' https://jwst-crds.stsci.edu/json/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Mon, 25 Jul 2016 20:03:13 GMT Vary: Cookie X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN Content-Type: application/json-rpc Via: 1.1 jwst-crds.stsci.edu Transfer-Encoding: chunked {"error": null, "jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": 1, "result": {"JW80500017001_02101_00001.MIRIFUSHORT": [true, ["jwst_miri_ipc_0005.fits", "jwst_miri_fringe_0018.fits", "jwst_miri_linearity_0010.fits", "jwst_miri_distortion_0010. asdf", "jwst_miri_specwcs_0003.asdf", "jwst_miri_drizpars_0001.fits", "jwst_miri_v2v3_0003.asdf", "jwst_miri_wavelengthrange_0001.asdf", "jwst_miri_regions_0003.asdf", "jwst_miri_wcsregions_0001.json", "jwst_miri_flat_0036.fits", "jwst_miri_saturation_0013.fits", "jwst_miri_photom_0011.fits", "jwst_miri_dark_0031.fits", "jwst_miri_gain_0004.fits", "jwst_miri_straymask_0006.fits", "jwst_miri_reset_0018.fits", "jwst_miri_lastframe_0018. fits", "jwst_miri_mask_0013.fits", "jwst_miri_readnoise_0005.fits"]]}}
Interface for Calibration S/W Versions
get_system_versions(master_version, context)
The versions of calibration software components for a particular s/w release will nominally be recorded in CRDS as reference files with type CALVER looked up from a corresponding rmap using a master version string. The function of this service is really independent of that representation, but nominally one reference file will describe versions for components of one s/w release.
This get_system_versions() service will return a JSON object corresponding to the contents of the s/w versions reference file. This interface should not however be construed as the definition of the file contents.
master_version is a string naming the overall version number for a calibration software release and used to select a particular versions reference file within a CRDS context.
context is a CRDS context name which is used to interpret master_version to define the versions reference file corresponding to an overall s/w release. Typically the string “null” should be used to select the current CRDS versions translation context in use in the JWST or Roman pipeline. It is anticipated that the definitions of software versions should be relatively stable and additive as new contexts are generated.
An example call using the CRDS Python client shows the conceptual nature of the interface, the functional inputs and outputs:
>>> versions_obj = get_system_versions("0.6.0noop.dev307", "null")
Printing the Python client return object in JSON format gives a more language agnostic view of the conceptual return value:
>>> print(json.dumps(versions_obj, indent=4, sort_keys=True)) { "CAL_VER": "0.6.0noop.dev307", "author": "Warren J. Hack", "descrip": "JWST calibration processing step version reference file", "history": "Created by cal_ver_steps version 0.7.0.dev", "instrument": "SYSTEM", "reftype": "CALVER", "versions": { "AlignRefsStep": null, "AmiAnalyzeStep": "0.7.0.dev", "AmiAverageStep": "0.7.0.dev", "AmiNormalizeStep": "0.7.0.dev", "AssignWcsStep": null, ... }, ... }
where indicates that the full contents of the object are not being
displayed.
The alternative abstract context identifier “jwst-versions” or “roman-versions” may be used in lieu of “null”. The translation of the “jwst-versions” or “roman-versions” identifier is maintained on the CRDS server as a more literal context name such as “jwst_0059.pmap”. The value associated with “jwst-versions” or “null” will nominally be updated on the CRDS server whenever a new master version is defined.
The intended purpose of the “jwst-versions” tag is to name the most capable context for use in translating calibration master versions. Unlike the abstract name “jwst-latest” that describes the default context used to define calibration references, it is anticipated that “jwst-versions” will never or rarely ever revert to older versions of CRDS rules. This is because “version facts” should not in general change once they’re defined, 0.6.0 should mean the same thing in every epoch, whereas it’s valid for calibration reference assignments to change over time.
Nevertheless, in the case of anomalous situations related to CAL_VER, alternate CRDS contexts may be explicitly named to specify different rules by which to translate master version names. Alternately, the value associated with “jwst-versions” (or “null”) can be redefined on the CRDS server.
The following curl command line shows the full expansion of the same service example wrapped in the JSONRPC protocol in a language agnostic way:
$ curl -i -X POST -d '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "method": "get_system_versions", "params": ["0.6.0noop.dev307","null"], "id": 1} ' https://jwst-crds-dit.stsci.edu/json/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Wed, 24 Aug 2016 22:33:04 GMT Vary: Cookie X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN Content-Type: application/json-rpc Via: 1.1 jwst-crds-dit.stsci.edu Transfer-Encoding: chunked {"error": null, "jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": 1, "result": {"reftype": "CALVER", "author": "Warren J. Hack", "versions": {"TweakRegStep": "0.1.0", "SubtractImagesStep": null, "RSCD_Step": null, "CubeBuildStep": null, "Extract1dStep": null, "AmiAnalyzeStep": "0.7.0.dev", "Extract2dStep": null, "BackgroundStep": null, "SuperBiasStep": null, "DarkCurrentStep": null, "Combine1dStep": null, "SaturationStep": null, "LinearityStep": null, "DQInitStep": null, "ImprintStep": null, "OutlierDetectionStep": null, "AssignWcsStep": null, "KlipStep": null, "StackRefsStep": null, "TweakregCatalogStep": null, "SourceCatalogStep": null, "PersistenceStep": null, "StraylightStep": null, "IPCStep": null, "FlatFieldStep": null, "ResetStep": null, "RefPixStep": null, "ResampleStep": null, "AmiAverageStep": "0.7.0.dev", "FringeStep": null, "AlignRefsStep": null, "LastFrameStep": null, "JumpStep": null, "EmissionStep": null, "WfsCombineStep": null, "AmiNormalizeStep": "0.7.0.dev", "SkyMatchStep": "0.1.0", "PhotomStep": null, "RampFitStep": null, "HlspStep": null}, "instrument": "SYSTEM", "descrip": "JWST calibration processing step version reference file", "CAL_VER": "0.6.0noop. dev307", "history": "Created by cal_ver_steps version 0.7.0.dev"}}
This example shows the structure of a response string for a query with an error, “result” is set to null and “error” describes the problem in more detail, most notably with the response.error.message string:
$ curl -i -X POST -d '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "method": "get_system_versions", "params": ["an,invalid(version)","null"], "id": 1}' https://jwst-crds-dit.stsci.edu/json/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Wed, 24 Aug 2016 22:23:11 GMT Vary: Cookie X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN Content-Type: application/json-rpc Via: 1.1 jwst-crds-dit.stsci.edu Transfer-Encoding: chunked {"error": {"message": "OtherError: Invalid version string, must be 1-128 chars of A-Z, a-z, 0-9, ., -, _", "code": 500, "data": null, "name": "OtherError"}, "jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": 1, "result": null}
JSONRPC Protocol
Sample URL’s
The base URL used for making CRDS JSONRPC method calls is essentially /json/. All further information, including the method name and the parameters, are POSTed using a JSON serialization scheme. Example absolute server URLs are:
$ http://hst-crds.stsci.edu/json/
$ http://jwst-crds.stsci.edu/json/
$ http://roman-crds.stsci.edu/json/
Generic Request
JSONRPC requests are made by POST’ing a set of variables to the appropriate URL.
An example CRDS service request can be demonstrated in a language agnostic way using the UNIX command line utility curl:
$ curl -i -X POST -d '{"jsonrpc": "1.0", "method": "get_default_context", "params": ["jwst"], "id": 1}' https://jwst-crds.stsci.edu/json/
The jsonrpc attribute is used to specify the version of the JSONRPC standard being used, currently 1.0 for CRDS.
The method attribute specifies the name of the service being called.
The params attribute specifies a JSON array of parameters which are passed positionally to the CRDS method.
The id can be used to associate calls with their responses in asynchronous environments.
Generic Response
The response returned by the server for the above request is the following JSON:
{"error": null, "jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": 1, "result": "jwst_0000.pmap"}
Error Handling
Fatal errors are handled by setting the error attribute of the result object to an error object. Inspect the result.error.message attribute to get descriptive text about the error.
Demo Page
The CRDS servers support demoing the JSONRPC services and calling them interactively by visiting the URL …/json/browse/. This facility is available in development and test environments upon request.
The resulting page is shown here:
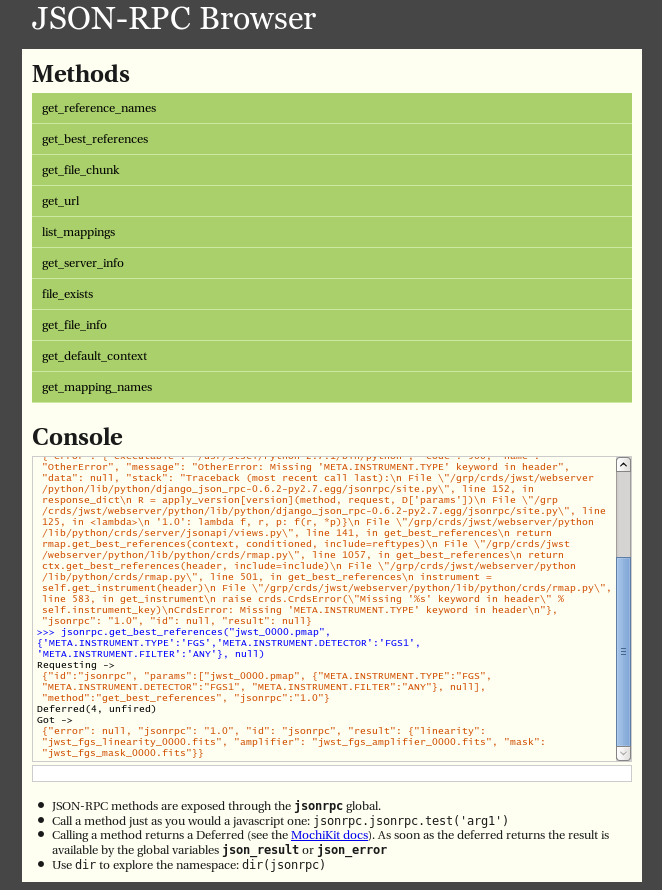
An example dialog for get_best_references from the CRDS jsonrpc demo page is shown here with FITS parkey names:
>>> jsonrpc.get_best_references("jwst_0000.pmap", {'INSTRUME':'FGS','DETECTOR':'FGS1', 'FILTER':'ANY'}, null)
Requesting ->
{"id":"jsonrpc", "params":["jwst_0000.pmap", {"INSTRUME":"FGS", "DETECTOR":"FGS1", "FILTER":"ANY"}, null], "method":"get_best_references", "jsonrpc":"1.0"}
Deferred(12, unfired)
Got ->
{"error": null, "jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": "jsonrpc", "result": {"linearity": "jwst_fgs_linearity_0000.fits", "amplifier": "jwst_fgs_amplifier_0000.fits", "mask": "jwst_fgs_mask_0000.fits"}}
And the same query is here with JWST data model parkey names:
>>> jsonrpc.get_best_references("jwst_0000.pmap", {'META.INSTRUMENT.TYPE':'FGS','META.INSTRUMENT.DETECTOR':'FGS1', 'META.INSTRUMENT.FILTER':'ANY'}, null)
Requesting ->
{"id":"jsonrpc", "params":["jwst_0000.pmap", {"META.INSTRUMENT.TYPE":"FGS", "META.INSTRUMENT.DETECTOR":"FGS1", "META.INSTRUMENT.FILTER":"ANY"}, null], "method":"get_best_references", "jsonrpc":"1.0"}
Deferred(14, unfired)
Got ->
{"error": null, "jsonrpc": "1.0", "id": "jsonrpc", "result": {"linearity": "jwst_fgs_linearity_0000.fits", "amplifier": "jwst_fgs_amplifier_0000.fits", "mask": "jwst_fgs_mask_0000.fits"}}